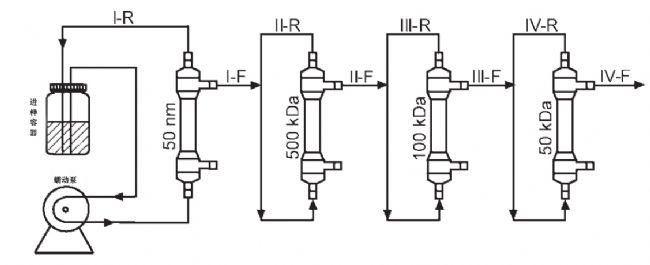
In modern medicine, blood transfusion is an important treatment for hemorrhagic shock, anemia and other diseases, and is also an important part of conventional surgery, but the risk of small-probability transmission such as hepatitis and AIDS always interferes with the safe operation of blood transfusion. In addition, before the blood transfusion, the donor blood should be typed and cross-matched with the recipient blood type to avoid rejection. In this regard, a relatively simple alternative is to replace donor red blood cells (RBCs) with hemoglobin (Hb) oxygen carriers (HBOCs), which have the following advantages: First, because there is no blood group antigen on the surface of HBOCs, it generally does not cause rowing. Different phenomena; secondly, the virus is inactivated and cleared during the purification of Hb, thus greatly reducing the possibility of transmission of blood-borne diseases. Hb is typically extracted from human or bovine RBCs (hRBCs or bRBCs). Chemical modification of purified Hb is one of the main pathways for the synthesis of HBOCs. Chemically modified HBOCs can be accomplished by intramolecular crosslinking of Hb, polymerization of Hb or binding of the polymer to the surface of Hb. Hb can also be embedded inside solid or hollow particles to form non-chemically modified HBOCs. Before extracting and purifying Hb from the lysed RBCs, the white blood cells, platelets and plasma components in the blood must be removed. The blood can be centrifuged and rinsed to separate the plasma and leukocyte layers. The resulting RBCs were then lysed by incubation with a hypotonic solution. There are many ways to purify Hb from RBC lysates, including organic solution extraction and ion exchange chromatography. The chromatographic method can in turn be broadly classified as an adsorption method (Hb is trapped in a solid phase medium and then solvent eluted) or a flow through method (impurities are trapped and Hb is eluted). The flow-through method eliminates the adsorption and elution processes, but the resulting Hb is less pure than the adsorption process. However, both methods are affected by the method of blood cell lysis and the state of lysis. Purification of Hb can also be carried out by heating under anaerobic conditions in the presence of a reducing agent. During this process, the heat sensitive protein is selectively precipitated, and the virus is inactivated, but Hb may also be inactivated due to high temperature, so it is necessary to add a stabilizer to prevent Hb denaturation. Filtration is also a common technique for Hb purification, which can effectively reduce the viral load in Hb solution. However, conventional filtration techniques typically require chemical modification and fractionation operations to separate the modified Hb from unmodified Hb and other impurities, and the flow rate is reduced due to cell debris clogging the pores of the membrane. In response to these questions, this article will introduce a multi-stage filtering method. In this method, most of the cell debris is removed in the first stage (membrane MWCO 50 nm) and then continuously filtered to gradually remove larger cell debris and molecules. This technique is relatively simple and allows simultaneous purification and concentration of Hb. KrosFlo Research 2 i [KR2 i ] Tangential Flow Filtration System Materials & Methods The initial treatment volume of the RBCs solution was 1,000 mL. After centrifugation, the non-cellular Hb and plasma proteins were removed by isotonic saline rinsing, and the RBCs were lysed with an ice bath of PB solution, and the final volume of the lysate was 2,000 mL. The instrument uses KrosFlo to develop a II i tangential flow filtration system and four hollow fiber filter modules of different pore sizes: 50nm, 500kD, 100kD and 50kD. The cascade flow path is shown in the figure below. The components are completely wetted with deionized water before use and tested for integrity. Schematic diagram of multi-stage hollow fiber filtration system At each filtration stage, the filtrate was collected and the reflux was circulated to increase Hb production. However, in stage III, 1 L of the PB solution was subjected to a washing operation. The entire purification process is carried out in a biosafety cabinet with the filtrate and reflux container placed on ice. The filtrate flow rate and transmembrane pressure were measured at the beginning and end of each stage, and after the end of each stage treatment, 10 mL was taken out from the filtrate for further analysis. Stage I initial filtration was 2,000 mL of RBCs lysate. At the end of each run, the HF assembly, associated hoses and containers were rinsed with 0.5 M NaOH solution to remove proteins that might adhere to the HF membrane and degrade endotoxin that may be present. The purified Hb was subjected to mass detection using Bradford, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and the like. Results & Discussion Due to concentration polarization, both the filtrate flow rate and the reflux volume decrease over time at each stage of Hb purification. Concentration polarization is due to the accumulation of macromolecules or particles on the surface of the HF membrane to form a filter cake layer. Even in the absence of physical clogging of the HF membrane, the formation of the filter cake layer reduces the rate at which molecules pass through the membrane. In the first two stages, most of the protein passes through the HF membrane and enters the filtrate container. The cell debris and macromolecules are concentrated and refluxed. Some of the cell debris will block the pores of the HF membrane, increase the transmembrane pressure and reduce the flow rate. In stage III, most of the Hb is trapped in the reflux and part of the Hb ([alpha][beta] dimer) enters the filtrate. Protein concentration analysis showed that most of the Hb was trapped in the reflux of Stage III (membrane MWCO 100kD) at a concentration of approximately 5 mM, significantly higher than the ion exchange chromatography method (0.7 - 1.7 mM), while the metHb level (~ 0.5%) Below the ion exchange chromatography method (0.5% - 2%). In purified Hb, the endotoxin level is also lower than that of RBCs. The endotoxin is mainly lipopolysaccharide (~10kD), which can be removed by filtration in stage III (100kD HF membrane). SDS-PAGE shows that most of the impurities can be removed in stages I and II, while in stage III, the level of impurities can be significantly reduced by continuous washing. In the equilibrium oxygen binding characteristics analysis, the measured values ​​of purified Hb (100 kD reflux) were close to those of RBCs, indicating that the TFF process did not change the Hb characteristics. The mass spectrometric detection of the contents of the phase III reflux liquid showed that the molecular weight detection values ​​of the α, β globulin chain and its polymer were consistent with the theoretical values, indicating that Hb is the main component in the phase III reflux liquid. Tangential flow filtration is a practical and rapid method for Hb purification and concentration. Compared with other methods, the obtained Hb has higher purity and lower metHb level. At the same time, adjusting the washing volume of stage III can further improve the purity of Hb. The content of this article is translated by the editor. If there is any inconvenience, please understand. For details, please refer to the original text. Original: Palmer, AF, et al.. Tangential Flow Filtration of Hemoglobin. Biotechnol. Prog., 2009, Vol. 25, No.1. Scan the QR code and pay attention to the official version of the WeChat public account to get more application information!
Medical Cold Patch
Patch For Diarrhea,Medicated Patches For Arthiritis,Plaster For Diarrhea,Pad For Diarrhea Shandong XiJieYiTong International Trade Co.,Ltd. , https://www.xjytmedical.com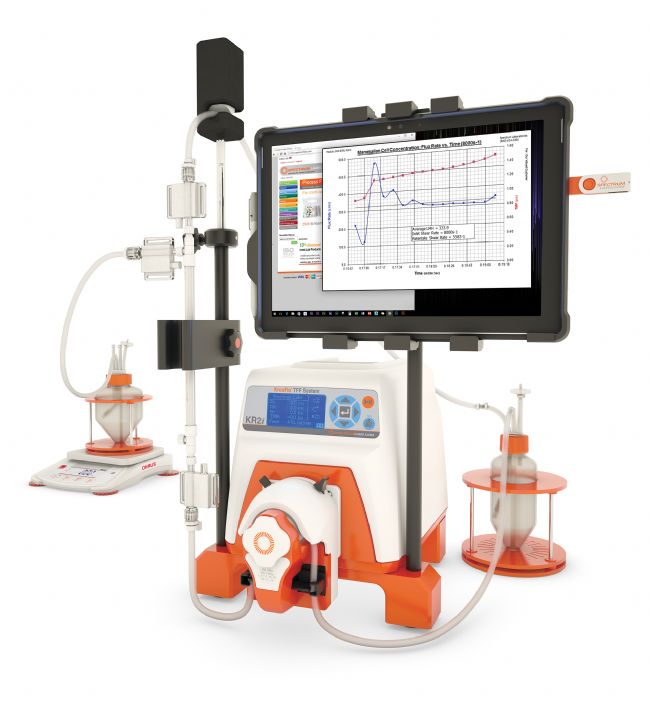

Patch for diarrhea
[Name] Medical Cold Patch
[Package Dimension] 5cm 4pieces/box
The pain relief patch is composed of three layers, namely, backing lining, middle gel and protective film. It is free from pharmacological, immunological or metabolic ingredients.
[Scope of Application] For cold physiotherapy, closed soft tissue only.
[Indications]
The patches give a fast relief for diarrhea.
[How To Use a Patch]
Please follow the Schematic Diagram. One piece, one time.
The curing effect of each piece can last for 6-8 hours.
[Attention]
Do not apply the patch on the problematic skin, such as wounds, eczema, dermatitis,or in the eyes. People allergic to herbs and the pregnant are advised not to use the medication. If swelling or irritation occurs, please stop using and if any of these effects persist or worsen.notify your doctor or pharmacist promptly. Children using the patch must be supervised by adults.
[Storage Conditions]
Store below 30c in a dry place away from heat and direct sunlight.