Laryngeal Mask,laryngeal mask airway,pvc laryngeal mask,disposable silicone laryngeal mask Anesthesia Medical Co., Ltd. , https://www.trustfulmedical.com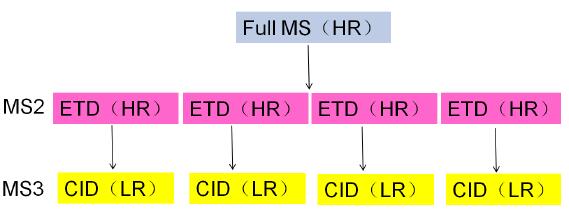
Application of ETD-triggered CID method to disulfide bond analysis of fusion proteins
Nie Aiying
Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co., Ltd.
Key words
Orbitrap Fusion; LTQ-Orbitrap series mass spectrometry; fusion protein Enbrel; ETD-triggered CID; disulfide bond analysis
1 Introduction
The fusion protein Enbrel (Etanercept) is a human TNF-α receptor synthesized by fusion of the extracellular receptor portion of human tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and human immunoglobulin (IgG1). The antibody fusion protein, which is an antagonist of tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), can inhibit inflammation and block the progression of the disease by inhibiting TNF-α. It is a DMARD drug and can be used for active rheumatoid arthritis. , psoriasis and joint psoriasis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and active ankylosing spondylitis.
The disulfide bond acts as a covalent bond to crosslink two cysteines in or between the polypeptide chains, which plays an important role in stabilizing the spatial structure of the protein, maintaining the correct spatial folding conformation, and maintaining and regulating its biological activity. Especially for biopharmaceuticals, the location and connection of disulfide bonds play a key role in the spatial structure and drug activity of biopharmaceuticals. At present, commonly used methods for locating disulfide bonds are mainly divided into X-ray diffraction crystal structure analysis method, multi-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance method, disulfide bond isomerization and mutation analysis method, enzymatic hydrolysis method and chemical cleavage method, etc., which have their own characteristics. , also have their own limitations. With the continuous development of mass spectrometry instruments in terms of quality detection range, resolution, sensitivity, accuracy and analysis speed, mass spectrometry is more suitable for the localization analysis of disulfide bonds. At present, commonly used mass spectrometry fragmentation techniques, including collision induced dissociation (CID), high energy collision dissociation (HCD), and electron transfer dissociation (ETD), can be directly applied to the fragmentation analysis of disulfide bonds, but different The fragmentation mode has its own characteristics for the cleavage of chemical bonds: ETD is more susceptible to disulfide bond cleavage between peptides, and CID is more susceptible to cleavage of peptide bonds in peptides, so the two are used together, that is, ETD-triggered CID. The method can firstly open the disulfide bond between the peptides through the ETD to obtain the disulfide bond connection information, and then use the CID to fragment the resolved peptide fragments, thereby obtaining the amino acid sequence of the peptide segment, so that In one experiment, the complete disulfide bond positioning information was obtained, as shown in Figure 1.
At present, the latest Orbitrap Fusion and LTQ-Orbitrap series of mass spectrometers combine the latest dual-pressure linear ion trap mass spectrometer with the new high-field Orbitrap TM mass analyzer to deliver ultra-high resolution and ultra-high sensitivity. Fast scanning speed and larger dynamic range, and low-resolution and high-resolution scanning can be performed simultaneously on the same mass spectrum, so that the above disulfide bond localization analysis can be performed for various protein samples, especially various Biopharmaceutical products, such as monoclonal antibodies and fusion proteins, provide accurate, fast and reliable analytical test methods and platforms.
Figure 1. Schematic of an ETD-triggered CID experiment applied to disulfide bond localization analysis (HR stands for high resolution scan and LR stands for low resolution scan)
2. Experimental part
2.1 Instruments and reagents
Mass Spectrometry Instruments: Orbitrap Fusion (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA);
Chromatography instrument: Easy Nano1000 LC system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA);
Column: Homemade reversed-phase column (C18, 2 μm, 75 × 150 μm, 100 Å);
Reagents: chromatographic grade formic acid, secondary deionized water, chromatographic grade acetonitrile.
2.2 Instrument method
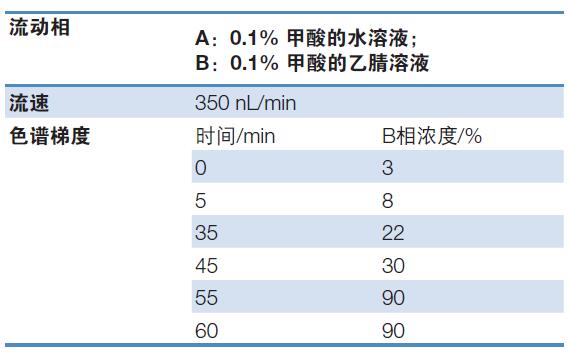
Chromatographic conditions: see Table 1 for details;
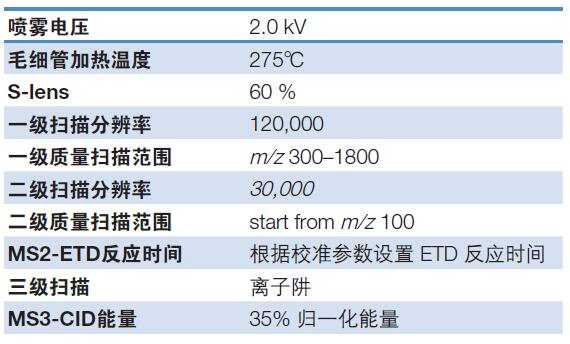
Mass spectrometry conditions: see Table 2 for details;
Table 1. Chromatographic conditions for fusion protein disulfide bond analysis
Table 2. Mass spectrometry conditions for fusion protein disulfide bond analysis
2.3 Data analysis methods
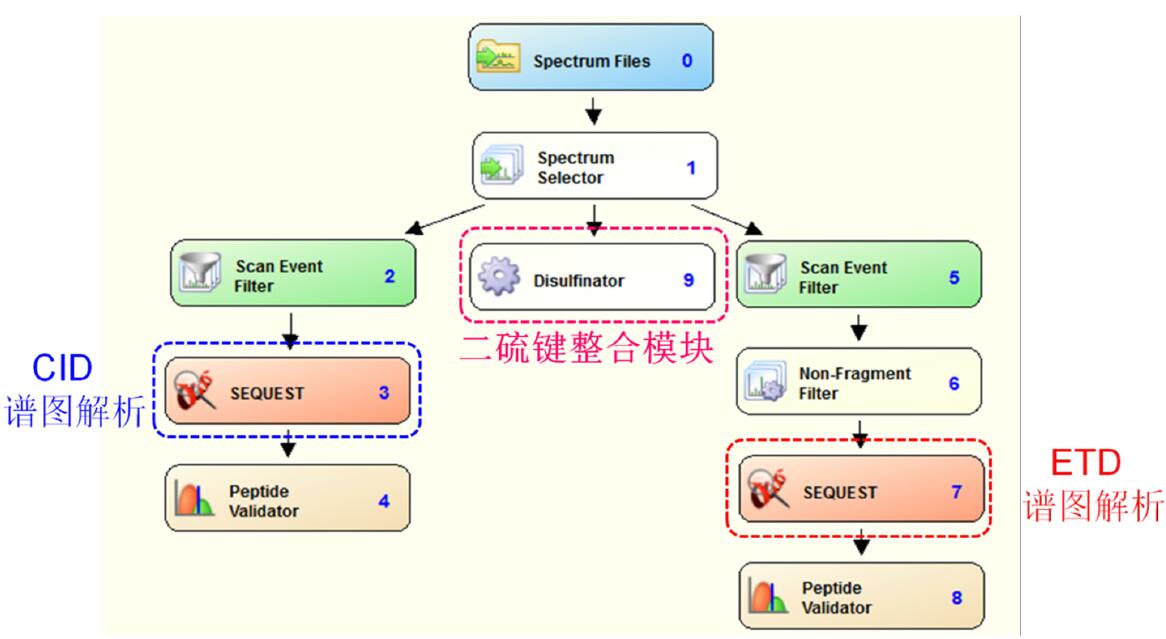
Use the Proteome Discoverer 1.3 software to perform a database search on the original spectrum. The specific parameters are as follows. The flow chart is shown in Figure 2:
Database: the amino acid sequence corresponding to the fusion protein;
Primary mass deviation: 20 ppm; secondary mass deviation: 0.02 Da; tertiary mass deviation: 0.8 Da;
Enzyme: trypsin+Chymotryspin;
Enzyme miss cleavage site: 2;
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the dite bond localization analysis of ETD-triggered CID raw data by Proteome Discoverer 1.3 software
3. Results and discussion
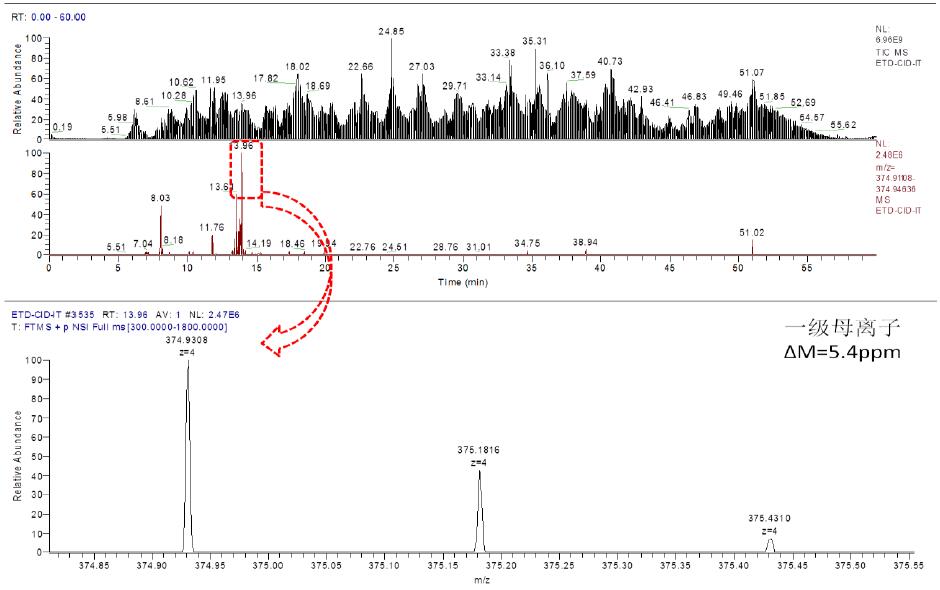
3.1 Taking the peptide P1:SKQEGCRL-peptide P2:CRPGF as an example:
a. Chromatographic mass spectrometry extraction flow diagram is as follows:
As can be seen from the above figure, the corresponding primary ion of the peptide eluted at 13.96 min, and the corresponding mass deviation was 5.4 ppm.
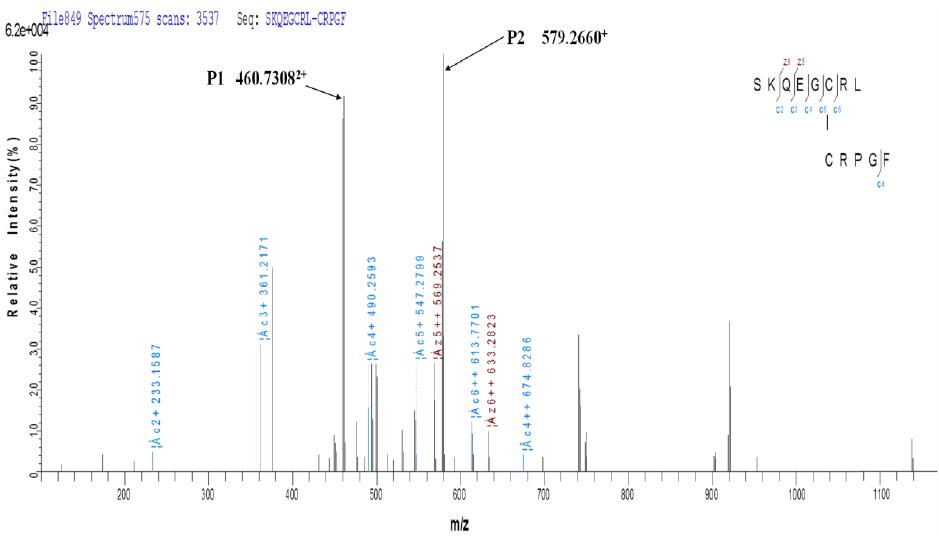
b. ETD secondary fragmentation matching map
It can be seen from the above figure that the two peptides linked by disulfide bond not only generate the fragment ions of the corresponding two peptides after fragmentation by ETD, but also produce other fragments with disulfide bonds connected together. Ion information.
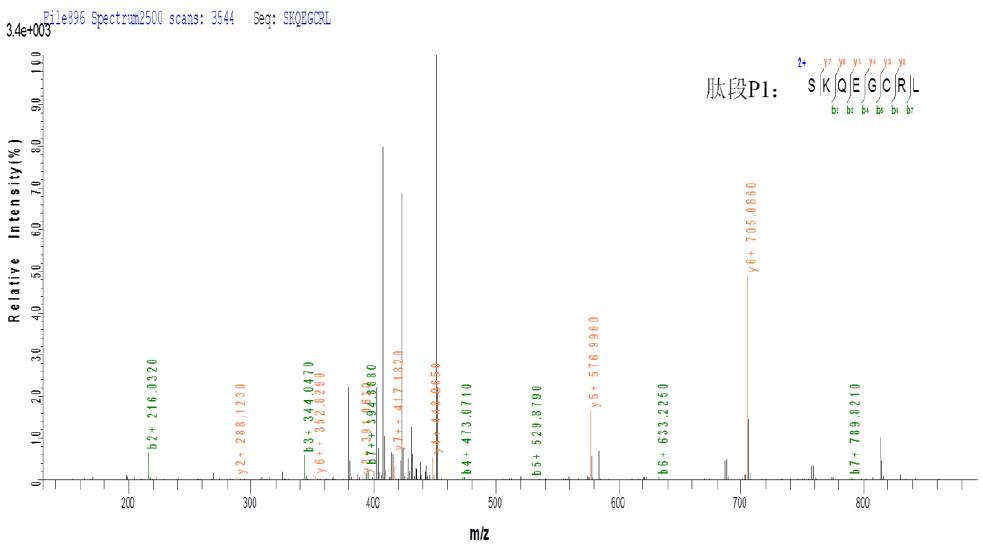
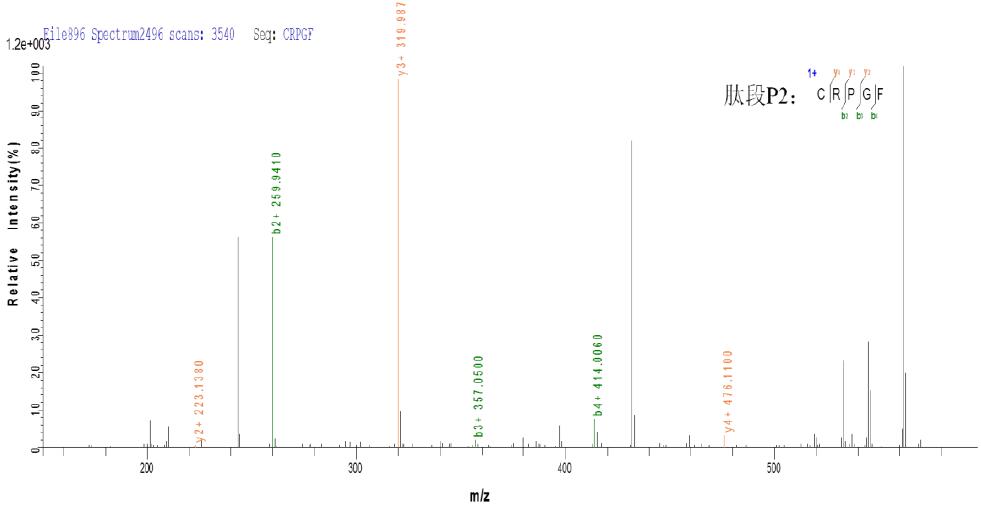
c. CID three-level fragmentation matching map
As can be seen from the above figure, the peptides P1 and P2 produced by ETD fragmentation generate a large number of b and y fragment ions in the subsequent three-stage CID fragmentation, which can effectively determine the composition of peptides P1 and P2, and combine Information on the ETD, thereby determining that the peptides P1 and P2 are linked together by disulfide bonds.
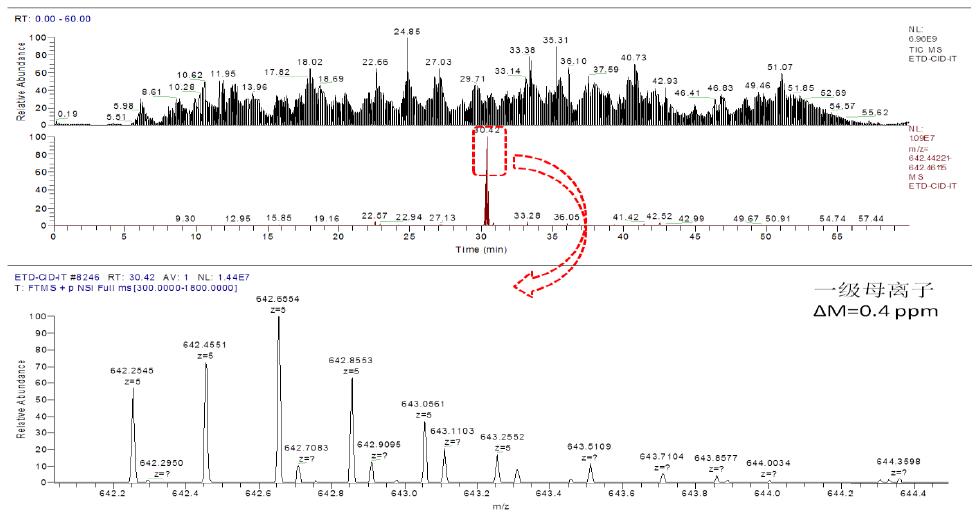
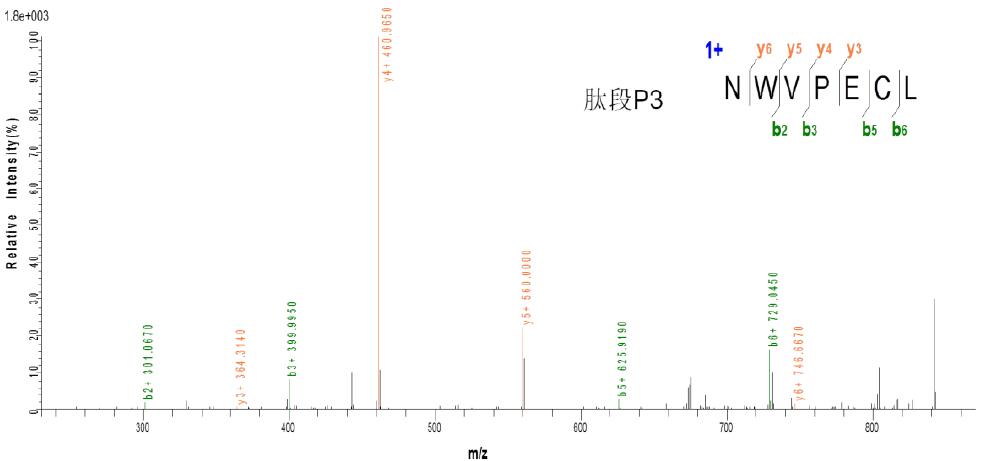
3.2 Taking peptide P1: CSPGQHAK - peptide P2: TSDTVCDSCEDSTY - peptide P3: NWVPECL as an example:
a. Chromatographic mass spectrometry extraction flow diagram is as follows:
As can be seen from the above figure, the corresponding primary ion of the peptide eluted at 30.42 min with a corresponding mass deviation of 0.4 ppm.
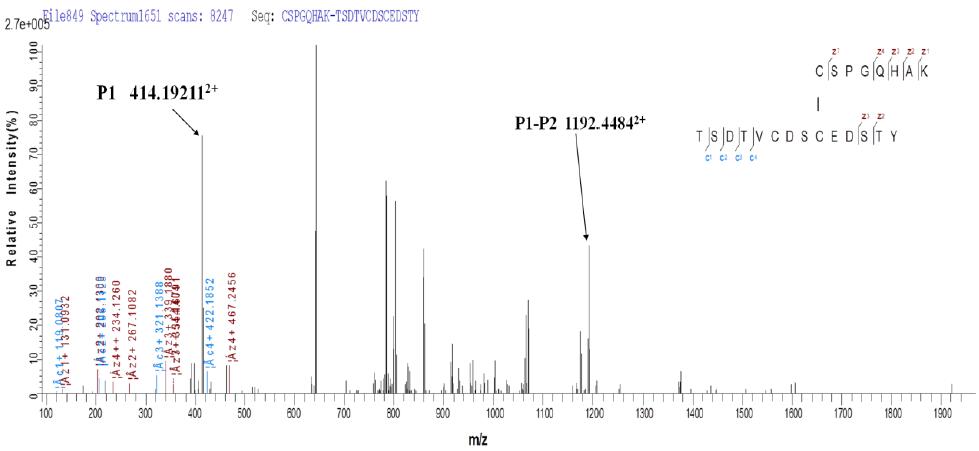
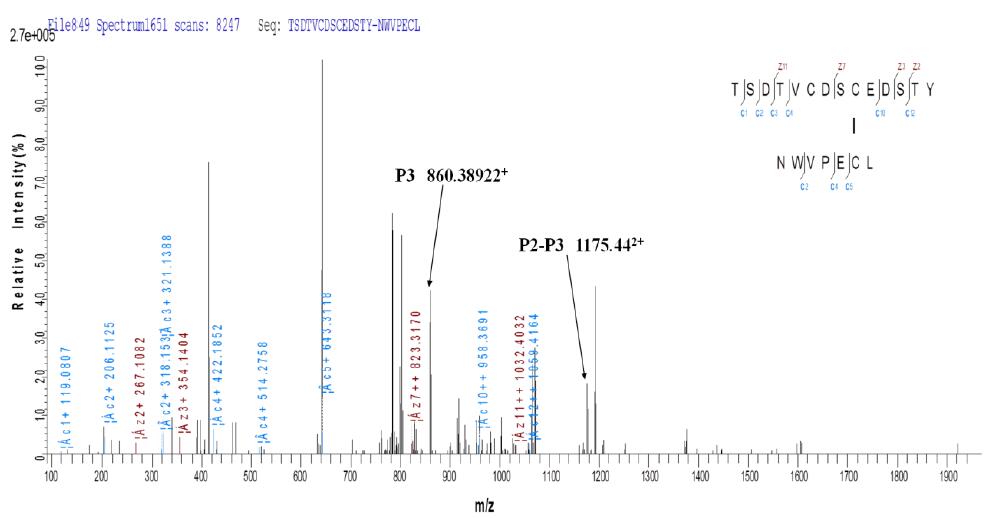
b. ETD secondary fragmentation matching map
Due to the limitations of current software, for the same ETD fragmentation spectrum, we performed two fragment ion labeling according to different disulfide linkages, and we can observe peptide P1, peptide P1-P2, peptide P3 and Peptide P2-P3, as indicated above. It can be seen that fragmentation by ETD not only produces fragment ions of the corresponding two peptides, but also generates other fragment ion information that the disulfide bonds are linked together.
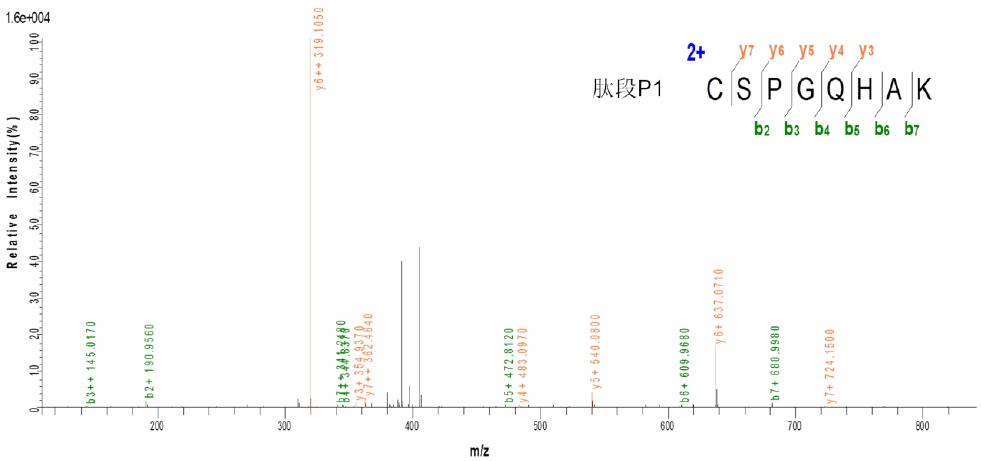
c. CID three-level fragmentation matching map
As can be seen from the above figure, the peptides P1 and P3 produced by ETD fragmentation generate a large number of b, y fragment ions in the subsequent three-stage CID fragmentation, so the presence of peptides P1 and P3 can be determined. It was found from the results that the peptide P2 was not effectively identified, which may be due to the presence of interchain disulfide bonds or the fragmentation or attachment of other chemical bonds during the fragmentation of disulfide bonds, but The above ETD and CID fragmentation information can be used to determine that there are indeed two pairs of interchain disulfide bonds between the three peptides.
4 Conclusion
In this paper, the disulfide bond analysis test method of ETD-triggered CID was established by Orbitrap-Fusion mass spectrometry, and the actual sample analysis was carried out in the sample of the fusion protein. Due to the limitation of the restriction site, trypsin and chymotrypsin were used. Enzymatic hydrolysis method can accurately determine most of the disulfide bond information existing, and also provide information on disulfide bond mismatch, providing an effective analytical test method for disulfide bond analysis of biopharmaceuticals such as monoclonal antibodies and fusion proteins. And platform. In addition, the combined mass spectrometers of the Orbitrap-Fusion and LTQ-Orbitrap series combine ultra-high resolution, ultra-fast scanning speed and high mass accuracy with a flexible approach and a variety of crushing methods. The cracking method has greatly improved and promoted the in-depth identification and quantitative analysis of mass spectrometry in the biopharmaceutical industry.